Biotech, short for biotechnology, is a broad field that encompasses living organisms or parts of living organisms to make products, improve plants or animals, or develop new processes for various industries. Biotech is a rapidly growing area with the potential to improve human health, agriculture, and the environment. In some instances, biotech and life sciences are used interchangeably, however, biotech is a subset of life science. Life science is a broader term that encompasses all the scientific disciplines that study living organisms, including biology, biochemistry, genetics, and microbiology.
Biotechnology is most applied in areas such as:
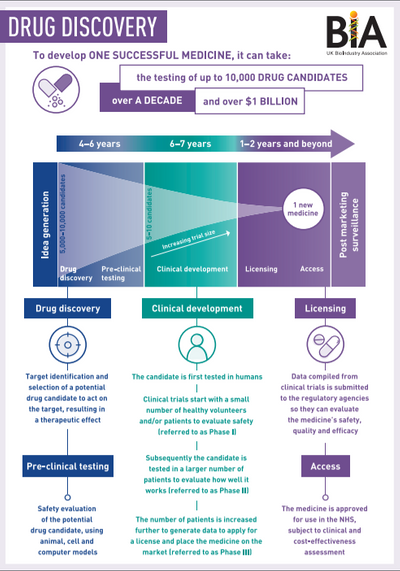
- Pharmaceuticals: Biotech plays a significant role in developing new drugs and vaccines. For example, the human insulin used to treat diabetes is made by genetically engineering bacteria to produce the insulin molecule.
- Agriculture: Biotech is used to improve crop yields, make crops more resistant to pests and diseases, and develop new food products. Such as Golden Rice is a genetically modified rice that is enriched with beta-carotene, which the body can convert into vitamin A.
- Environmental cleanup: Biotech is used to clean up pollution and restore damaged ecosystems, where bacteria can be used to break down oil spills, and plants can be used to filter pollutants from water.
- Energy production: Biotech is being used to develop new sources of energy, such as biofuels and biogas. For example, ethanol is a biofuel that can be made from corn or other plants.
Benefits and risks of biotech
Biotech has numerous benefits including improved human health with life-saving drugs and therapies for various diseases; increased food production and nutritional value of foods; environmental sustainability and industrial applications (enzymes, bioplastics, and other bio-based materials) as well as advances in research and development enabling scientists to understand diseases, unravel genetic complexities and develop novel treatments.
Despite the many benefits of biotechnology, there are also some concerns about risks that could come as the sector grows. These include ethical concerns, environmental impact, regulatory challenges, economic disparities as well as human health and safety. The most popular concern being the use of human genes in animals and misuse for harmful purposes, such as developing biological weapons.
It is worth noting that these risks are not inherent to biotechnology itself but rather associated with its applications and the way it is utilised. With responsible research, robust regulations, and careful consideration of ethical implications, many of these risks can be managed effectively.
History and future of biotechnology
Biotechnology has been around for centuries, but it has only been in the last few decades that it has become a major field of scientific research and development. There are many different aspects of biotechnology, including agricultural biotechnology, medical biotechnology, and environmental biotechnology. The biotech sector is rapidly growing with the potential to bring the next wave of human revolution and civilisation.
The UK biotech industry
The UK's innovative life sciences and biotech industry delivers ground-breaking treatments to patients. Companies, including BIA members, create novel therapies and diagnostics that will help treat and manage conditions to enable people to lead quality lives.
From investing in and carrying out research and development to getting drugs from the lab and into patients, the UK biotech and life science industry plays a central role in developing the treatments needed for future generations here and around the globe.